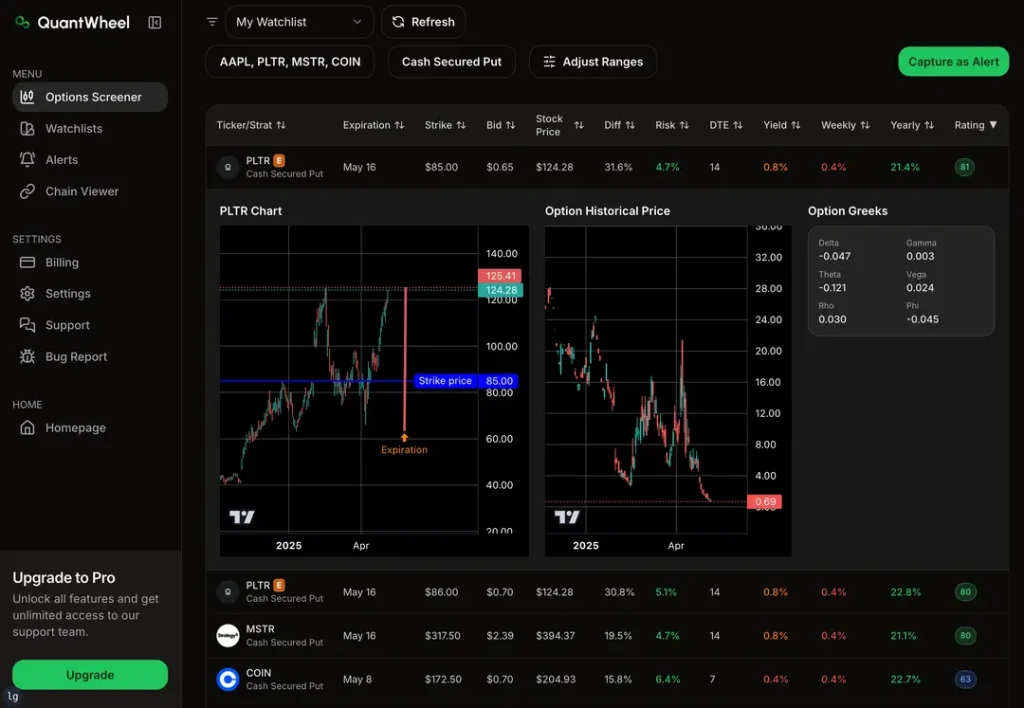
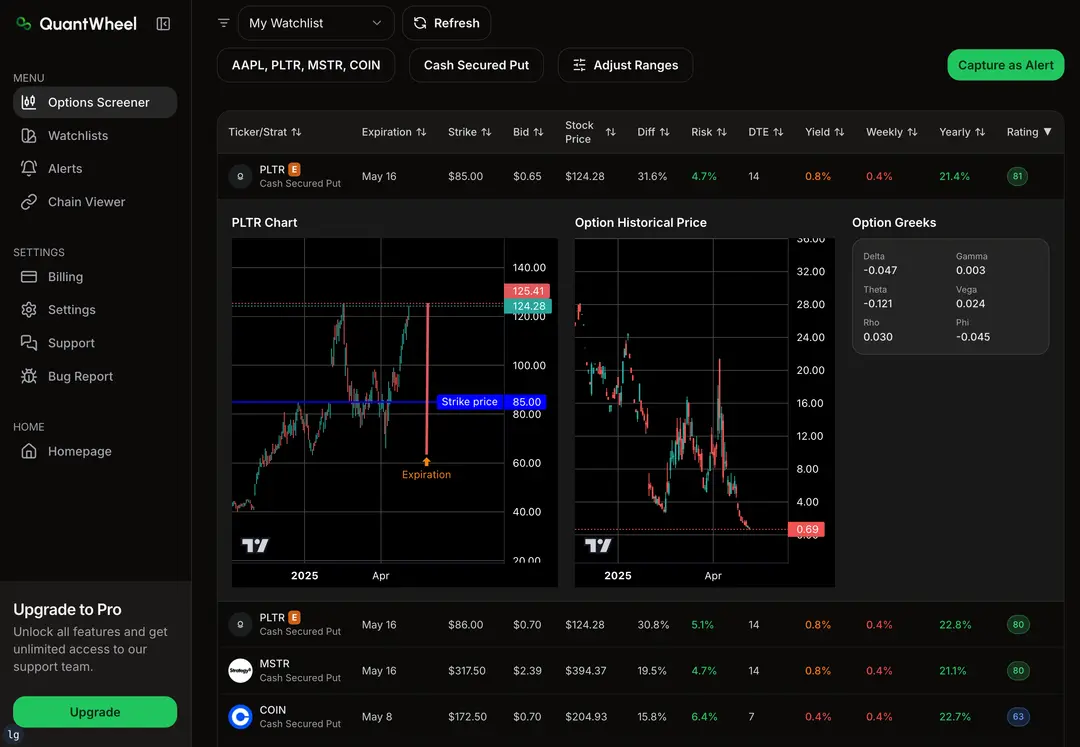
For the beginners in options trading there is always the one question that typically gets answered last – what are greeks in options trading?
Let’s get to it.
Options Greeks are tools that help you understand how different factors affect the price of options. They measure the sensitivity of an option’s price to things like changes in the stock price, time, and market volatility. Knowing these can improve your ability to make smart investment decisions.
Each Greek looks at a specific part of the market. For example, Delta shows how much an option’s price moves when the stock price changes. Theta tells you how time affects the option’s value. Learning to read these signals helps you predict option price changes better.
Understanding options Greeks is key if you want to trade options wisely. This article breaks down the main Greeks and shows how you can use them in your trading strategies.
Understanding the Options Greeks
Options Greeks measure how option prices change based on different factors. They help you manage risk and understand how your option contracts react to changes in the stock price, time, and market conditions. Paying attention to these can improve your investment decisions.
Delta and Its Significance
Delta shows how much your option’s price changes when the underlying stock price moves by $1. For example, a delta of 0.5 means the option’s price will increase by about $0.50 if the stock price rises by $1.
Call options have positive delta, while put options have negative delta. Delta also indicates the chance that an option will expire in the money. A delta near 1 or -1 means a high chance, while near 0 means low.
Traders use delta to estimate price risk and to hedge their positions. It can guide when to buy or sell options or the underlying asset.
Gamma and Price Sensitivity
Gamma measures how fast delta changes when the stock price moves. It shows the rate of change in sensitivity, giving you insight into how stable your delta is.
High gamma means delta can shift quickly with small price moves, which increases unpredictability in option value. This mostly happens when the stock price is close to the option’s strike price.
You use gamma to estimate risk and to adjust hedges. If you want steady exposure, lower gamma is safer. If you’re trading around strike prices, gamma helps predict rapid price swings.
Theta and Time Decay
Theta shows how much your option price falls as time passes with all else constant. Options lose value as expiration approaches, especially for out-of-the-money options.
A theta of -0.05 means your option loses 5 cents in value every day, assuming the stock price stays the same. Time decay speeds up near expiration.
Understanding theta lets you manage timing risk and decide when to sell or exercise options. It also impacts strategies like writing options where you earn premium as time passes.
Vega and Volatility Response
Vega measures how an option’s price changes when the underlying stock’s volatility changes by 1%. Higher volatility usually boosts option prices.
If you have a vega of 0.10, a 1% rise in volatility will increase your option price by about 10 cents. Vega is highest for at-the-money options and longer expiration times.
You track vega to see how market uncertainty affects your option value. When volatility rises, option prices increase, which can be good for buyers and risky for sellers. Vega helps in risk management and pricing derivatives effectively.
Practical Applications and Strategies
Understanding how the Greeks affect options can help you protect your money, manage risk, and make smarter trades. You can use this knowledge to adjust your positions, either to limit losses or to boost gains. It also helps you decide when to buy or sell calls and puts.
Hedging and Risk Management
You use Greeks to hedge your portfolio by balancing risk. For example, Delta shows how much your option price changes when the stock moves. If you hold shares, buying puts with a negative Delta can protect against losses.
Theta tells you how much value your options lose each day due to time decay. Traders watch this to avoid heavy losses from holding options too long.
Vega measures sensitivity to volatility. If you expect market swings, you can buy options with a high Vega to gain if volatility rises, or sell to collect premium if you expect calm markets.
Greeks in Options Trading
Each Greek affects your trading differently. Delta helps you pick how much of the underlying asset your position covers. For example, if Delta is 0.5, one option moves half as much as the stock.
Gamma tells you how Delta changes when the price moves. It’s important for adjusting positions often. High Gamma means Delta is very sensitive, so your risk changes fast.
Theta is a key factor in strategies like selling options, because you earn money as time passes and the option loses value.
Vega and Rho track volatility and interest rates. Though less visible day-to-day, they matter in longer-term trades or when market conditions change.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Knowing Greeks guides when to enter or exit trades. If you want steady income, you might sell calls with high Theta for premium collection.
If you expect big stock moves, buying options with high Vega benefits from rising volatility.
You can also manage leverage better. Instead of buying many shares, options let you control more assets with less money, but Greeks help you understand the risk behind this leverage.
Using Greeks, you decide how much risk fits your money and goals. This keeps your investments safer and your trading more informed.