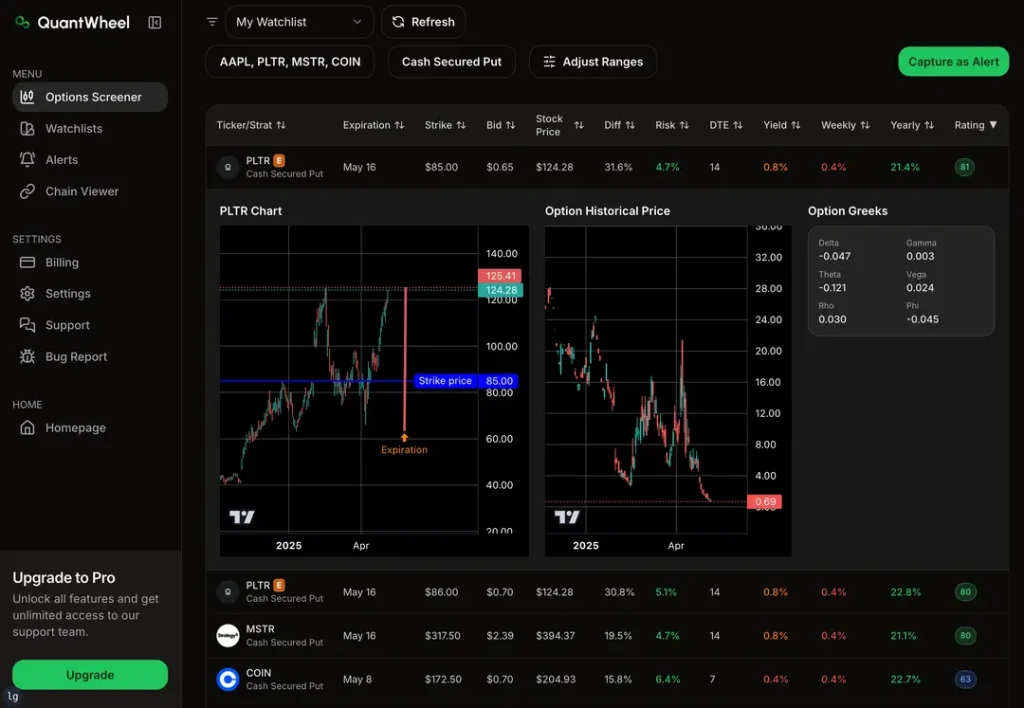
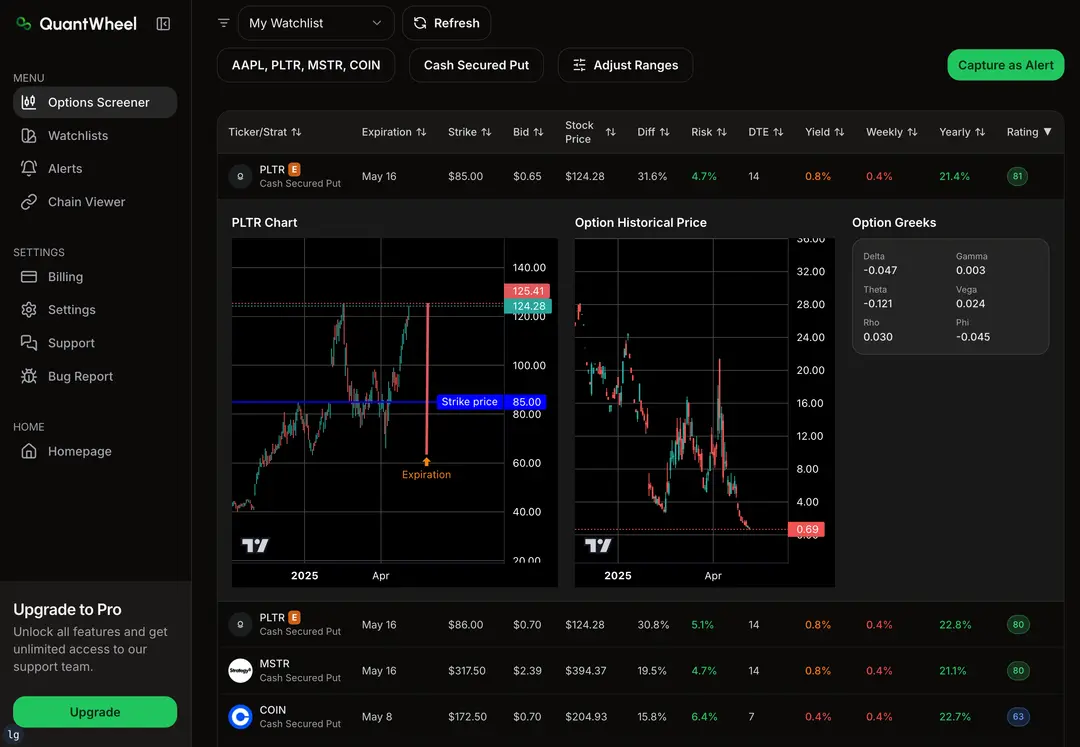
What are the benefits and what can you do with options?
Options give you additional possibilities with what you can do with stocks – resulting in squeezing out more profit from them or reducing your risk.
Unlike buying stocks directly, you can use options to generate income, protect your investments, or speculate on price changes with clear maximum losses.
Basically – they are an “add-on” to stocks that offer extreme flexibility.
Options are hard to compare since they have many uses, but one area in which you can compare them is that they give additional leverage.
Just as you can enter a classic buy or sell position in Crypto or Forex, or enter a leveraged buy or sell position (like most traders do) – you can do the same with options on stocks.
Basically, they are an “add-on” to classic buying or selling stocks, just like the leverage is an “add-on” to trading Forex pairs and Crypto pairs.
But, that’s just one part of them.
What options unlock additionally is:
1) you can earn even if the stock isn’t moving,
2) earn by letting others take the risk of trading
3) earn by “protecting your position” – pay a small fee to lock in a max loss that protects you if things go wrong, while keeping all the profits if things go right
Suddenly, from being just a regular knife, you become a swiss knife..
What Are Options? Definition for Beginners
Let’s start with a formal definition – options are contracts that give you the right to buy or sell an asset at a certain strike price by a set expiration date.
This basically means that they are bets that you can place with time expirations.
Below are some ways in which traders use options.
There are 4 different scenarios options can be used for:
1) Leverage Mode
-
-
- Options let you control 100 shares with much less capital – just like in Crypto where you can get 50:1 to 500:1 leverage,
- Instead of buying stock → buy a call option (bullish, like going long)
- Instead of shorting stock → buy a put option (bearish, like going short)
-
It’s like being the casino instead of the gambler – consistent small wins instead of big directional bets.
2) Income Mode (this doesn’t exist in forex/crypto/futures)
-
-
- Instead of betting on direction, you become the “house” – selling contracts to other traders and collecting premiums.
- Time works FOR you instead of against you – contracts of people who buy options lose value every day, and you keep that money if you are selling them.
-
It’s like being the casino instead of the gambler – consistent small wins instead of big directional bets.
3) Sideways Market Mode (impossible in forex/crypto/futures)
-
-
- In forex/futures, if the market doesn’t move, you make nothing (or lose on spread/fees).
- With options, you can profit when the market stays flat using different strategies. (more on that later).
-
You’re basically betting on what WON’T happen instead of what will happen.
4) Insurance Mode (hedging without closing positions)
-
-
- Unlike in other trading styles where you hedge by taking an opposite position, options let you protect profits without selling your stock.
- You keep your winning position open (no taxes triggered) while buying protection against a drop.
-
It’s like having stop-losses that don’t force you to exit – you stay in the trade but limit your downside.
Why Trade Options? 5 Key Advantages Over Stock Trading
1) Lower Capital Requirements
If used a certain way (buying calls or puts) options usually need less money to profit much more than you would profit with stocks. You can control 100 shares of stock for the price of a single option contract. This leaves you with extra cash for other investments. More buying power, less money out of your pocket. Neat.
2) Built-in Risk Management
When you’re buying options, you set your maximum loss before you even make the trade. This is a big advantage when compared to other types of trading.
Unlike stocks that could drop to zero, your risk is capped at the premium you paid when you buy options (bet on a stock going up or down).
That helps protect you from big losses.
In forex or crypto where the leverage is used by 80% of the traders, a sudden 10% move against you forces you out of the trade through liquidation.
With buying options, your maximum loss is capped at what you paid upfront—nothing worse can happen.
You know exactly how much you can lose before you enter, so you control your risk much better than in forex or crypto.
This makes options trading much more risk friendly than other types of trading, as long as you don’t gamble.
What’s important to know is that you can also sell options, the risk here is defined differently, but when looked from the statistical standpoint – options sellers win 80% of their trades.
More on this later.
3) Higher Profit Potential
When buying options, they use leverage to boost your returns. Even a small move in a stock can lead to big percentage gains in options.
For example, a 10% move in a stock might mean a 60% profit on your option.
That can really amplify your returns when things go your way.
Note:
This applies only if you’re buying options and that way betting on the direction.
For selling options – you typically earn less, but you win more often so it adds up over time.
4) More Trading Strategies
Options give you ways to make money whether stocks go up, down, or just sit still – isn’t that cool?
Popular strategies include:
-
-
- Buying calls if you think stocks will rise
- Buying puts if you expect stocks to fall
- Writing/selling covered calls for extra income
- Selling cash-secured puts for income
- Using spreads to limit risk
-
Don’t worry, these are just fancy terms, you can learn them later.
5) Flexible Position Management
You can adjust your options trades as the market changes. Different strategies let you tweak your risk and profit targets as you go.
There are also several ways to exit a trade.
That flexibility helps you adapt if the market surprises you.
Imagine that – full flexibility, no matter what happens on the market.
Options vs Stocks: Key Differences for Beginners
When you buy stocks, you own a piece of a company.
That means you get a share of its assets and maybe even a vote.
Options are different, you don’t participate in the business directly but you can earn by being right.
You bet on stock performance because you believe some “outside events” will or will not affect the stock.
Ownership and Control
Stocks make you a shareholder with voting rights. Options don’t give you ownership until you use them. (it’s enough to just be aware of this)
Money Required
Options cost way less up front than stocks.
One contract controls 100 shares, but you only pay a fraction of what buying those shares would cost.
This is good if you’re using options to make directional trades (betting on a stock going up or down).
If you’re willing to “rent stocks” or act as an “insurance company”, therefore let others take on the risk of trading – that’s also possible.
But, you have to have a little deeper pockets in order to do that.
I personally use the second option more.
Risk and Loss
With stocks, you risk losing everything if the company tanks. Your loss matches the stock’s drop.
Options have different risks depending on if you sell options or buy options.
If you buy options:
You can lose only the money you paid for the option, but that’s it—the loss is limited to your premium.
This is good if you’re using options to make directional trades (betting on a stock going up or down).
If you’re not willing to bet on a direction and want a safer route, risk is even lower – selling options.
If you sell options:
It requires you to have deeper pockets because certain strategies require you to actually own the stock or at least for you to be willing to buy it if the trade goes badly.
This can be portrayed as more risky but in reality is less risky.
Option buyers lose 80% of time on their trades and they’re okay with that, options sellers on the other hand win 80% of the time.
The conclusion:
Don’t pick sides (selling vs buying options). Adapt to market.
Time Limits
Stocks don’t expire. You can hold shares as long as the company survives. Options expire on set dates. If you don’t use your option by then, it just goes to zero. This means that you have to have your timing right.
Profit Potential
Stock profits come from price increases and sometimes dividends. Options can make money from price moves in either direction or even when stock doesn’t move an inch. Options also work for assets like ETFs. Each security brings different possibilities for your investment plans.